About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 208 results for "Marc Choisy" clear search
Peer reviewed Family Herd Demography
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Rebecca Garabed Abigail Buffington | Published Monday, August 15, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The model examines the dynamics of herd growth in African pastoral systems. We used it to examine the role of scale (herd size) stochasticity (in mortality, fertility, and offtake) on herd growth.
Lewis' Signaling Chains
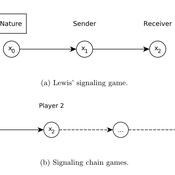
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
Leviathan group model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Tuesday, July 26, 2022The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) with the addition of group idenetity. We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. Moreover, each agent belongs to a single group and the opinions within the group are attracted to their average.
We show that a group hierarchy can emerges from this model, and that the inequality of reputations among groups have a negative effect on the opinions about the groups of low status. The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the group, the more detrimental the interactions with the agents of other groups are for the opinions about this group, especially when gossip is activated. However, the interactions between agents of the same group tend to have a positive effect on the opinions about this group.
Peer reviewed SIM-VOLATILE: Adoption of emerging circular technologies in the waste-treatment sector
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Wednesday, December 14, 2022The SIM-VOLATILE model is a technology adoption model at the population level. The technology, in this model, is called Volatile Fatty Acid Platform (VFAP) and it is in the frame of the circular economy. The technology is considered an emerging technology and it is in the optimization phase. Through the adoption of VFAP, waste-treatment plants will be able to convert organic waste into high-end products rather than focusing on the production of biogas. Moreover, there are three adoption/investment scenarios as the technology enables the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), single-cell oils (SCO), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). However, due to differences in the processing related to the products, waste-treatment plants need to choose one adoption scenario.
In this simulation, there are several parameters and variables. Agents are heterogeneous waste-treatment plants that face the problem of circular economy technology adoption. Since the technology is emerging, the adoption decision is associated with high risks. In this regard, first, agents evaluate the economic feasibility of the emerging technology for each product (investment scenarios). Second, they will check on the trend of adoption in their social environment (i.e. local pressure for each scenario). Third, they combine these two economic and social assessments with an environmental assessment which is their environmental decision-value (i.e. their status on green technology). This combination gives the agent an overall adaptability fitness value (detailed for each scenario). If this value is above a certain threshold, agents may decide to adopt the emerging technology, which is ultimately depending on their predominant adoption probabilities and market gaps.
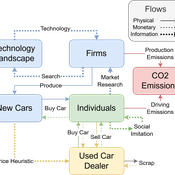
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
University Connectivity
Rachel Wozniak Nick Glover Chris English Juan Cisneros | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021This model is designed to show the effects of personality types and student organizations have on ones chance to making friendships in a university setting. As known from psychology studies, those that are extroverted have an easier chance making friendships in comparison to those that are introverted.
Once every tick a pair of students (nodes) will be randomly selected they will then have the chance to either be come friends or not (create an edge or not) based on their personality type (you are able to change what the effect of each personality is) and whether or not they are in the same club (you can change this value) then the model triggers the next tick cycle to begin.
Market for Protection
Steven Doubleday | Published Monday, July 01, 2013 | Last modified Monday, August 19, 2013Simulation to replicate and extend an analytical model (Konrad & Skaperdas, 2010) of the provision of security as a collective good. We simulate bandits preying upon peasants in an anarchy condition.
The Pampas Model: An agent-based model of agricultural systems in the Argentinean Pampas
Michael North Federico Bert Guillermo P Podestá Santiago L Rovere Charles Macal | Published Tuesday, July 16, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 17, 2015The Pampas Model is an Agent-Based Model intended to explore the dynamics of structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the Argentine Pampas in response to climatic, technological economic, and political drivers.
Political Participation
Didier Ruedin | Published Saturday, April 12, 2014 | Last modified Sunday, September 28, 2025Implementation of Milbrath’s (1965) model of political participation. Individual participation is determined by stimuli from the political environment, interpersonal interaction, as well as individual characteristics.
CONSERVAT
Pieter Van Oel | Published Monday, April 13, 2015The CONSERVAT model evaluates the effect of social influence among farmers in the Lake Naivasha basin (Kenya) on the spatiotemporal diffusion pattern of soil conservation effort levels and the resulting reduction in lake sedimentation.
Displaying 10 of 208 results for "Marc Choisy" clear search