About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 940 results for "Ibo van de Poel" clear search
CITMOD A Tax-Benefit Modeling System for the average citizen
Philip Truscott | Published Monday, August 15, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Must tax-benefit policy making be limited to the ‘experts’?
Interactions between organizations and social networks in common-pool resource governance
Phesi Project | Published Monday, October 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Explores how social networks affect implementation of institutional rules in a common pool resource.
Agents’ beliefs and the evolution of institutions for common-pool resource management
Giangiacomo Bravo | Published Friday, December 17, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013C++ and Netlogo models presented in G. Bravo (2011), “Agents’ beliefs and the evolution of institutions for common-pool resource management”. Rationality and Society 23(1).
Peer reviewed SWIRS Spread of a woody invader in riparian systems
Moira Zellner Beatriz Sosa Carlos Andrés Chiale | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023Riparian forests are one of the most vulnerable ecosystems to the development of biological invasions, therefore limiting their spread is one of the main challenges for conservation. The main factors that explain plant invasions in these ecosystems are the capacity for both short- and long-distance seed dispersion, and the occurrence of suitable habitats that facilitate the establishment of the invasive species. Large floods constitute an abiotic filter for invasion.
This model simulates the spatio-temporal spread of the woody invader Gleditsia. triacanthos in the riparian forest of the National Park Esteros de Farrapos e Islas del Río Uruguay, a riparian system in the coast of the Uruguay river (South America). In this model, we represent different environmental conditions for the development of G. triacanthos, long- and short-distance spread of its fruits, and large floods as the main factor of mortality for fruit and early stages.
Field results show that the distribution pattern of this invasive species is limited by establishment, i.e. it spreads locally through the expansion of small areas, and remotely through new invasion foci. This model recreates this dispersion pattern. We use this model to derive management implications to control the spread of G. triacanthos
Foragers to Farmers
Nick Gauthier Elske van der Vaart Michael Storozum Tim Dorscheidt | Published Monday, July 22, 2024This model is represents an effort to replicate one of the first attempts (van der Vaart 2006) to develop an agent based model of agricultural origins using principles and equations drawn from human behavioral ecology. We have taken one theory of habitat choice (Ideal Free Distribution) and applied it to human behavioral adaptations to differences in resource quality of different habitats.
Peer reviewed Multilevel Group Selection I
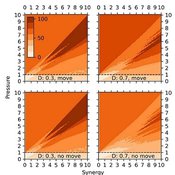
Wayne W. Wakeland Thaddeus Shannon Garry Sotnik | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Saturday, July 03, 2021New theoretical agent-based model of population-wide adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior with four parameters (initial percent of adopters, pressure to change behavior, synergy from behavior, and population density); dynamics in behavior, movement, freeriding, and group composition and size; and emergence of multilevel group selection. Theoretical analysis of model’s dynamics identified six regions in model’s parameter space, in which pressure-synergy combinations lead to different outcomes: extinction, persistence, and full adoption. Simulation results verified the theoretical analysis and demonstrated that increases in density reduce number of pressure-synergy combinations leading to population-wide adoption; initial percent of contributors affects underlying behavior and final outcomes, but not size of regions or transition zones between them; and random movement assists adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior.
Peer reviewed Evolution of Cooperation in Asymmetric Commons Dilemmas
Marco Janssen Nathan Rollins | Published Friday, August 20, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model can be used to explore under which conditions agents behave as observed in field experiments on irrigation games.
Spatial model of the noisy Prisoner's Dilemma with reward shift
Matus Halas | Published Thursday, March 05, 2015 | Last modified Tuesday, May 29, 2018Interactions of players embedded in a closed square lattice are determined by distance and overall gains and they lead to shifts of reward payoff between temptation and punishment. A new winner balancing against threats is ultimately discovered.
Agent-based Modelling of Unsustainable and Sustainable Norms Under Resource Constraints
Fachrizal Sinaga Adrian Thomas Sufyan Fawwad | Published Monday, November 24, 2025This model explores the coupled dynamics of social norm diffusion and finite resource depletion. Extending the “Affordance Landscape” framework by Kaaronen & Strelkovskii (2020), this simulation investigates how resource scarcity and regeneration rates influence the adoption of pro-environmental behaviours.
The model addresses the gap by linking behavioural norms to a depleting common-pool resource. It tests whether sustainable norms can diffuse rapidly enough to prevent ecological collapse and identifies “tipping points” where resource scarcity acts as a driver for behavioural change.
Peer reviewed AgentEx
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Caroline Schill Therese Lindahl | Published Sunday, November 13, 2016AgentEx aims to advance understanding of group processes for sustainable management of a common pool resource (CPR). By supporting the development and test explanations of cooperation and sustainable exploitation.
Displaying 10 of 940 results for "Ibo van de Poel" clear search