About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
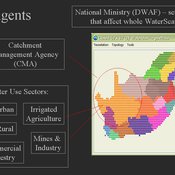
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Effective population size and cultural evolution
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 17, 2016This model illustrates how the effective population size and the rate of change in mean skill level of a cultural trait are affected by the presence of natural selection and/or the cultural transmission mechanism by which it is passed.
Perceived Scientific Value and Impact Factor
Davide Secchi Stephen J Cowley | Published Wednesday, April 12, 2017 | Last modified Monday, January 29, 2018The model explores the impact of journal metrics (e.g., the notorious impact factor) on the perception that academics have of an article’s scientific value.
An ABM of historic British milk consumption
Matthew Gibson | Published Monday, December 20, 2021Substitution of food products will be key to realising widespread adoption of sustainable diets. We present an agent-based model of decision-making and influences on food choice, and apply it to historically observed trends of British whole and skimmed (including semi) milk consumption from 1974 to 2005. We aim to give a plausible representation of milk choice substitution, and test different mechanisms of choice consideration. Agents are consumers that perceive information regarding the two milk choices, and hold values that inform their position on the health and environmental impact of those choices. Habit, social influence and post-decision evaluation are modelled. Representative survey data on human values and long-running public concerns empirically inform the model. An experiment was run to compare two model variants by how they perform in reproducing these trends. This was measured by recording mean weekly milk consumption per person. The variants differed in how agents became disposed to consider alternative milk choices. One followed a threshold approach, the other was probability based. All other model aspects remained unchanged. An optimisation exercise via an evolutionary algorithm was used to calibrate the model variants independently to observed data. Following calibration, uncertainty and global variance-based temporal sensitivity analysis were conducted. Both model variants were able to reproduce the general pattern of historical milk consumption, however, the probability-based approach gave a closer fit to the observed data, but over a wider range of uncertainty. This responds to, and further highlights, the need for research that looks at, and compares, different models of human decision-making in agent-based and simulation models. This study is the first to present an agent-based modelling of food choice substitution in the context of British milk consumption. It can serve as a valuable pre-curser to the modelling of dietary shift and sustainable product substitution to plant-based alternatives in Britain.
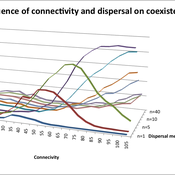
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
AMMA: Agent-based Model of the Media Arena
Annie Waldherr | Published Tuesday, February 11, 2014The AMMA simulates how news waves emerge in the mass media. Drawing on the ideas of public arena models and issue-attention cycles, it represents fundamental principles of public communication in a virtual media system.
Peer reviewed Umwelten Ants
Kit Martin | Published Thursday, January 15, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, August 27, 2015Simulates impacts of ants killing colony mates when in conflict with another nest. The murder rate is adjustable, and the environmental change is variable. The colonies employ social learning so knowledge diffusion proceeds if interactions occur.
The purpose of this model is to enhance a basic ABM through a simple set of rules identified using the activity-driven models in order to produce more realistic patterns of pedestrian movement.
Ageing and Spending
Tony Lawson | Published Tuesday, October 06, 2015How natural population ageing affects UK household spending patterns.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search