About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search
Hominin Ecodynamics v.1.1 (update for perception and interaction)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, August 15, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Models land-use, perception, and biocultural interactions between two forager populations.
Mobility, Resource Harvesting and Robustness of Social-Ecological Systems
Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Monday, September 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is a stylized representation of a social-ecological system of agents moving and harvesting a renewable resource. The purpose is to analyze how mobility affects sustainability. Experiments changing agents’ mobility, landscape and information governments have can be run.
Variations on the Ethnocentrism Model of Hammond and Axelrod
Fredrik Jansson | Published Saturday, November 10, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Agents co-operate or defect towards other agents in a prisoner’s dilemma, with strategy choice depending on whether agents share tags or are kin in different social structures.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Exploring Creativity and Urban Development with Agent-Based Modeling
Ammar Malik Andrew Crooks Hilton Root Melanie Swartz | Published Thursday, October 30, 2014An agent-based model which explores Creativity and Urban Development
DINO model - Dynamics of Internalization and Dissemination of Norms
Marlene Batzke | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2023 | Last modified Saturday, August 19, 2023The DINO model (Dynamics of Internalization and Dissemimnation of Norms) simulates a conceptual model on the dynamics of norm internalization in the decision-making framework of a 3-person prisoner’s dilemma game.
Peer reviewed Theoretical Model of Oak Persistence Under Competition and Herbivory
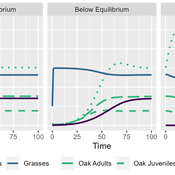
MV Eitzel Solera | Published Tuesday, October 25, 2022This model is intended to support oak tree management by representing the dynamics of oaks in multiple life stages and their competitors and consumers. This is implemented using a differential equation-based theoretical model representing three life stages of oaks: seedlings, juveniles, and adults. It includes the population dynamics of seedlings transitioning to juveniles, juveniles to adults, and adults producing new seedlings, as well as survival rates for each of the stages. It also includes a model of competition for light and water within seedlings and between seedlings and annual grasses. Finally, there is a predation term representing herbivores eating seedlings and grasses, using a Holling Type II (satiating) response with interference for predators and a death rate which depends on the resource extraction rate.
Peer reviewed Environmental stochasticity, resource heterogeneity, and the evolution of cooperation
Michaela Starkey Colin Lynch Terry Hunt Carl Lipo | Published Friday, March 14, 2025 | Last modified Wednesday, July 30, 2025The emergence of cooperation in human societies is often linked to environmental constraints, yet the specific conditions that promote cooperative behavior remain an open question. This study examines how resource unpredictability and spatial dispersion influence the evolution of cooperation using an agent-based model (ABM). Our simulations test the effects of rainfall variability and resource distribution on the survival of cooperative and non-cooperative strategies. The results show that cooperation is most likely to emerge when resources are patchy, widely spaced, and rainfall is unpredictable. In these environments, non-cooperators rapidly deplete local resources and face high mortality when forced to migrate between distant patches. In contrast, cooperators—who store and share resources—can better endure extended droughts and irregular resource availability. While rainfall stochasticity alone does not directly select for cooperation, its interaction with resource patchiness and spatial constraints creates conditions where cooperative strategies provide a survival advantage. These findings offer broader insights into how environmental uncertainty shapes social organization in resource-limited settings. By integrating ecological constraints into computational modeling, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of the conditions that drive cooperation across diverse human and animal systems.
Individual time preferences and adoption of destructive extraction methods
Marco Janssen Aneeque Javaid Hauke Reuter Achim Schlueter | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016We model the relationship between natural resource user´s individual time preferences and their use of destructive extraction method in the context of small-scale fisheries.
Peer reviewed Modelling the Social Complexity of Reputation and Status Dynamics
André Grow Andreas Flache | Published Wednesday, February 01, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, January 23, 2019The purpose of this model is to illustrate the use of agent-based computational modelling in the study of the emergence of reputation and status beliefs in a population.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search