About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 549 results for "Niklas Hase" clear search
A Mathematical Model of The Beer Game
Hakan Yasarcan Mert Edali | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014This is the R code of the mathematical model that includes the decision making formulations for artificial agents. This code corresponds to equations 1-70 given in the paper “A Mathematical Model of The Beer Game”.
Sugarscape with spice
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Friday, September 18, 2020This is a variation of the Sugarspace model of Axtell and Epstein (1996) with spice and trade of sugar and spice. The model is not an exact replication since we have a somewhat simpler landscape of sugar and spice resources included, as well as a simple reproduction rule where agents with a certain accumulated wealth derive an offspring (if a nearby empty patch is available).
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/
Simulating changing traffic flow caused by new bus route in Augsburg
Eduard | Published Wednesday, August 04, 2021This is a Netlogo model which simulates car and bus/tram traffic in Augsburg, specifically between the districts Stadtbergen, Göggingen and the Königsplatz. People either use their cars or public transport to travel to one of their random destinations (Stadtbergen or Göggingen), performing some activity and then returning to their home. Attributes such as travel and waiting time as well as their happiness upon arriving are stored and have an impact on individuals on whether they would consider changing their mode of transport or not.
Multi-Hazard Coastal Agent-Based Model (MHCABM)
Andrew Allison | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021MHCABM is an agent-based, multi-hazard risk interaction model with an integrated applied dynamic adaptive pathways planning component. It is designed to explore the impacts of climate change adaptation decisions on the form and function of a coastal human-environment system, using as a case study an idealised patch based representation of the Mount North-Omanu area of Tauranga city, New Zealand. The interacting hazards represented are erosion, inundation, groundwater intrusion driven by intermittent heavy rainfall / inundations (storm) impacts, and sea level rise.
Multi-agent model of the spread of climate change denial
Kalina Maria Piskorska Martin Takáč | Published Monday, March 03, 2025This NetLogo model simulates the spread of climate change beliefs within a population of individuals. Each believer has an initial belief level, which changes over time due to interactions with other individuals and exposure to media. The aim of the model is to identify possible methods for reducing climate change denial.
Optimal Trading Strategies of Agents in a Population of Firms: An Agent-Based Approach to Soccer Transfer Markets
Kehinde Salau | Published Tuesday, December 16, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Default Initial skill, read ODD for more info. The purpose of the model presented by Salau is to study the ’player profit vs. club benefit’ dilemma present in professional soccer organizations.
Schelling Model of the City of Salzburg
Andreas Schlagbauer | Published Monday, December 05, 2022The purpose of the model is to better understand, how different factors for human residential choices affect the city’s segregation pattern. Therefore, a Schelling (1971) model was extended to include ethnicity, income, and affordability and applied to the city of Salzburg. So far, only a few studies have tried to explore the effect of multiple factors on the residential pattern (Sahasranaman & Jensen, 2016, 2018; Yin, 2009). Thereby, models using multiple factors can produce more realistic results (Benenson et al., 2002). This model and the corresponding thesis aim to fill that gap.
Equity Constrained Dispatching Model of Emergency Medical Services
Sreekanth V K Ram Babu Roy | Published Thursday, September 08, 2016 | Last modified Monday, May 01, 2017Model for evaluating various ambulance dispatching policies of an equity constrained emergency medical services under bounded rationality.
Salzburg Bicycle model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016An ABM to simulate the spatio-temporal distribution of cyclists across the road network of the city of Salzburg.
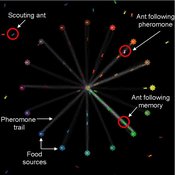
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
Displaying 10 of 549 results for "Niklas Hase" clear search