About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
Neminem laedere: Socially damaging behaviours and how to contain them
Nicola Lettieri | Published Wednesday, June 23, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013First version of the model “Neminem laedere. Socially damaging behaviours and how to contain them” by Domenico Parisi and Nicola Lettieri
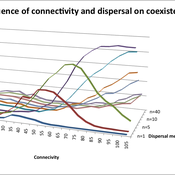
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
Homophily and Distance Depending Network Generation for Modelling Opinion Dynamics
Sascha Holzhauer | Published Wednesday, August 22, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, June 18, 2013The model uses opinion dynamics to test a simple and ecient but empirically based approach for generating social networks in spatial agent-based models which explicitly takes into account restrictions and opportunities imposed by effects of baseline homophily and considers the probability of links that depends on geographical distance between potential partners.
Seasonal Social Networks and Learning Opportunities Under Unbiased Cultural Transmission
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Monday, May 18, 2015This agent-based model examines the impact of seasonal aggregation, dispersion, and learning opportunities on the richness and evenness of artifact styles under random social learning (unbiased transmission).
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
The influence of cognitive diversity on networked search and coordination
César García-Díaz | Published Wednesday, April 03, 2024Agent-based models of organizational search have long investigated how exploitative and exploratory behaviors shape and affect performance on complex landscapes. To explore this further, we build a series of models where agents have different levels of expertise and cognitive capabilities, so they must rely on each other’s knowledge to navigate the landscape. Model A investigates performance results for efficient and inefficient networks. Building on Model B, it adds individual-level cognitive diversity and interaction based on knowledge similarity. Model C then explores the performance implications of coordination spaces. Results show that totally connected networks outperform both hierarchical and clustered network structures when there are clear signals to detect neighbor performance. However, this pattern is reversed when agents must rely on experiential search and follow a path-dependent exploration pattern.
The doctrinal paradox in deliberative process and in majority voting
Sacha Ferrari | Published Monday, January 13, 2025This model proposes a new approach analyzing to the doctrinal paradox by considering a deliberative process (which can be represented by an agent-based model) in comparison with classical (binary) majority voting and an aggregation of (continuous) degrees of belief prior to majority voting. This model is a multivariate extension of the Hegselmann–Krause opinion dynamics model.
A model on feeding and social interaction behaviour of pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans | Published Thursday, May 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, February 27, 2018The model simulates interaction between internal physiological factors (e.g. energy balance) and external social factors (e.g. competition level) underlying feeding and social interaction behaviour of commercially group-housed pigs.
Impact of topography and climate change on Magdalenian social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Monday, September 11, 2017The model presented here was created as part of my dissertation. It aims to study the impacts of topography and climate change on prehistoric networks, with a focus on the Magdalenian, which is dated to between 20 and 14,000 years ago.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search