About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1185 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
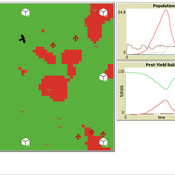
Peer reviewed Avian pest control: Yield outcome due to insectivorous birds, falconry, and integration of nest boxes.
David Jung | Published Monday, November 13, 2023 | Last modified Sunday, November 19, 2023The model aims to simulate predator-prey relationships in an agricultural setting. The focus lies on avian communities and their effect on different pest organisms (here: pest birds, rodents, and arthropod pests). Since most case studies focused on the impact on arthropod pests (AP) alone, this model attempts to include effects on yield outcome. By incorporating three treatments with different factor levels (insectivorous bird species, falconry, nest box density) an experimental setup is given that allows for further statistical analysis to identify an optimal combination of the treatments.
In light of a global decline of birds, insects, and many other groups of organisms, alternative practices of pest management are heavily needed to reduce the input of pesticides. Avian pest control therefore poses an opportunity to bridge the disconnect between humans and nature by realizing ecosystem services and emphasizing sustainable social ecological systems.
Geographic Expansion Model (GEM)
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, February 28, 2020The purpose of this model is to explore the importance of geographic factors to the settlement choices of early Neolithic agriculturalists. In the model, each agriculturalist spreads to one of the best locations within a modeler specified radius. The best location is determined by choosing either one factor such as elevation or slope; or by ranking geographic factors in order of importance.
Village level varietal dynamics of Sorghum in Mali
Geraldine Abrami | Published Thursday, December 03, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Final project version - still needs a bit of work for being completly operational
Nudging agents in social networks for collective action
Marco Janssen | Published Sunday, August 14, 2011 | Last modified Sunday, March 17, 2019Agents are linked in a social-network and make decisions on which of 2 types of behavior to adopt. We explore consequences of different information feedback and providing targeted feedback to individuals.
An Agent-Based Model of Corruption: Micro Approach
Valery Dzutsati | Published Friday, January 30, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, September 27, 2015Endogenous social transition from a high-corruption state to a low-corruption state, replication of Hammond 2009
A Consumer in the Jungle of Product Differentiation
Alessandro Pluchino Andrea Rapisarda Alessio Emanuele Biondo Alfio Giarlotta | Published Tuesday, December 22, 2015Building upon the distance-based Hotelling’s differentiation idea, we describe the behavioral experience of several prototypes of consumers, who walk a hypothetical cognitive path in an attempt to maximize their satisfaction.
Simulation of Self-enforcing Agreement in Cooperative Teams
Hang Xiong | Published Friday, April 01, 2016This is an agent-based model of the implementation of the self-enforcing agreement in cooperative teams.
HMODEL: an exploratory simulation of surface archaeological formation
Benjamin Davies Simon Holdaway Patricia Fanning | Published Thursday, November 30, 2017This model is used to simulate the influence of spatially and temporally variable sedimentary processes on the distribution of dated archaeological features in a surface context.
High Standards Enhance Inequality in Idealized Labor Markets
Károly Takács | Published Tuesday, March 20, 2018Takács, K. and Squazzoni, F. 2015. High Standards Enhance Inequality in Idealized Labor Markets. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 18(4), 2, http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/18/4/2.html
We built a simple model of an idealized labor market, in which there is no objective difference in average quality between groups and hiring decisions are not biased in favor of any particular group. Our results show that inequality in employment emerges necessarily also in such idealized situations due to the limited supply of high quality individuals and asymmetric information. Inequalities are exacerbated when employers have high standards and keep only the best workers in house. We found that ambitious workers get higher quality jobs even if ambition does not correlate or even negatively correlates with internal quality. Our findings help to corroborate empirical findings on higher employment discrepancies in high rather than low status jobs.
Displaying 10 of 1185 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search