About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 541 results for "Viet Cao" clear search
Opinion dynamics and collective risk perception: An ABM model of institutional and media communication about disasters - Code and Datasets
danielevilone | Published Tuesday, October 06, 2020The O.R.E. (Opinions on Risky Events) model describes how a population of interacting individuals process information about a risk of natural catastrophe. The institutional information gives the official evaluation of the risk; the agents receive this communication, process it and also speak to each other processing further the information. The description of the algorithm (as it appears also in the paper) can be found in the attached file OREmodel_description.pdf.
The code (ORE_model.c), written in C, is commented. Also the datasets (inputFACEBOOK.txt and inputEMAILs.txt) of the real networks utilized with this model are available.
For any questions/requests, please write me at [email protected]
Unification-Conditions-of-Civilization-Patterns-Multi-Agent-Modeling-of-Human-History
zhuo zhang | Published Friday, May 27, 2022 | Last modified Sunday, May 29, 2022The model of Chinese and Western civilization patterns can help understand how civilizations formed, how they evolved by themselves, and the difference between the unity of China and the disunity of the Western. The previous research had examined historical phenomena about civilization patterns with subjective, static, local, and inductive methods. Therefore, we propose a general model of history dynamics for civilizations pattern, which contains both China and the West, to improve our understanding of civilization formation and the factors influencing the pattern of civilization. And at the same time, the model is used to find the boundary conditions of two different patterns.
Informal Information Transmission Networks among Medieval Genoese Investors
Christopher Frantz | Published Wednesday, October 09, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 24, 2013This model represents informal information transmission networks among medieval Genoese investors used to inform each other about cheating merchants they employed as part of long-distance trade operations.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
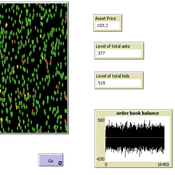
Peer reviewed A financial market with zero intelligence agents
edgarkp | Published Wednesday, March 27, 2024The model’s aim is to represent the price dynamics under very simple market conditions, given the values adopted by the user for the model parameters. We suppose the market of a financial asset contains agents on the hypothesis they have zero-intelligence. In each period, a certain amount of agents are randomly selected to participate to the market. Each of these agents decides, in a equiprobable way, between proposing to make a transaction (talk = 1) or not (talk = 0). Again in an equiprobable way, each participating agent decides to speak on the supply (ask) or the demand side (bid) of the market, and proposes a volume of assets, where this number is drawn randomly from a uniform distribution. The granularity depends on various factors, including market conventions, the type of assets or goods being traded, and regulatory requirements. In some markets, high granularity is essential to capture small price movements accurately, while in others, coarser granularity is sufficient due to the nature of the assets or goods being traded
ManPraSim: A Management Practice Simulation
peer-olaf_siebers | Published Wednesday, February 23, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This simulation model is associated with the journal paper “A First Approach on Modelling Staff Proactiveness in Retail Simulation Models” to appear in the Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 14 (2) 2. The authors are Peer-Olaf Siebers ([email protected]) and Uwe Aickelin ([email protected]).
An Agent-Based Model of Internet Diffusion Under General and Specific Network Externalities
Filiz Garip | Published Friday, April 27, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Using nodes from the 2002 General Social Survey sample, the code establishes a network of ties with a given homophily bias, and simulates Internet adoption rates in that network under three conditions: (i) no network externalities, (ii) general network externalities, where an individual’s reservation price is a function of the overall adoption rate in the network, (iii) specific network externalities, where reservation price is a function of the adoption rate in individual’s personal […]
SearchResource
Romulus-Catalin Damaceanu | Published Friday, May 04, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An algorithm implemented in NetLogo that can be used for searching resources.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
A-KinGDom: A Kinship, Grooming and Dominance Model for Primate Societies
Ruth Dolado Francesc S Beltran Vicenc Quera | Published Thursday, July 11, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 17, 2013A-KinGDom simulates the emergence of the social structure in a group of non-human primates. The model includes dominance and affiliative interactions which allow us to define four different attack and affiliative strategies.
Displaying 10 of 541 results for "Viet Cao" clear search