About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 69 results for "L Ballato" clear search
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
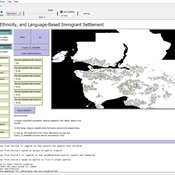
Geospatial Agent-Based Model of Immigrant Settlement Dynamics in Metro Vancouver
Liliana Perez Navid Mahdizadeh Gharakhanlou Maryam Yousefi | Published Wednesday, December 03, 2025This agent-based model simulates how new immigrant households choose where to live in Metro Vancouver under the origins diversity scenario. The model begins with 16,000 household agents, reflecting an expected annual population increase of about 42,500 people based on an average household size of 2.56. Each agent is assigned four characteristics: one of ten origin categories, income level (adjusted using NOC data and recent immigrant earnings), likelihood of having children, and preferred mode of commuting. The ten origin groups are drawn from Census patterns, including six subgroups within the broader Asian category (China, India, the Philippines, Iran, South Korea, and Other Asian countries) and two categories for immigrants from the Americas. This refined classification better captures the diversity of newcomers arriving in the region.
DITCH --- A Model of Inter-Ethnic Partnership Formation
Ruth Meyer Laurence Lessard-Phillips Huw Vasey | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, February 02, 2016The DITCH model has been developed to investigate partner selection processes, focusing on individual preferences, opportunities for contact, and group size to uncover how these may lead to differential rates of inter-ethnic marriage.
Peer reviewed Population Genetics
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, September 09, 2020This model simulates the mechanisms of evolution, or how allele frequencies change in a population over time.
Agent-based model of sexual partnership
Andrea Knittel | Published Monday, December 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In this model agents meet, evaluate one another, decide whether or not to date, if and when to become sexual partners, and when to break up.
Modeling information Asymmetries in Tourism
Jacopo A. Baggio Rodolfo Baggio | Published Monday, January 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A very simple model elaborated to explore what may happens when buyers (travelers) have more information than sellers (tourist destinations)
Central-place forager mobility and cultural diversity
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2016This spatially explicit agent-based model addresses how effective foraging radius (r_e) affects the effective size–and thus the equilibrium cultural diversity–of a structured population composed of central-place foraging groups.
An agent-based simulation of discussion processes in risk workshops
Matthias Meyer Clemens Harten Lucia Bellora-Bienengräber | Published Thursday, September 30, 2021The model measures drivers of effectiveness of risk assessments in risk workshops regarding the correctness and required time. Specifically, we model the limits to information transfer, incomplete discussions, group characteristics, and interaction patterns and investigate their effect on risk assessment in risk workshops.
The model simulates a discussion in the context of a risk workshop with 9 participants. The participants use Bayesian networks to assess a given risk individually and as a group.
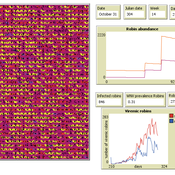
Peer reviewed AMRO_CULEX_WNV
Aniruddha Belsare Jennifer Owen | Published Saturday, February 27, 2021 | Last modified Thursday, March 11, 2021An agent-based model simulating West Nile Virus dynamics in a one host (American robin)-one vector (Culex spp. mosquito) system. ODD improved and code cleaned.
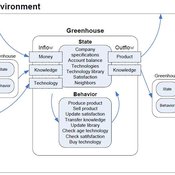
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Displaying 10 of 69 results for "L Ballato" clear search