About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 810 results for "Jon Solera" clear search
An epidemiological-economic agent-based model of Huanglongbing and Asian citrus psyllid control in California
Jonathan Kaplan | Published Wednesday, June 01, 2022This model simulates economic and epidemiological interaction between citrus production and the disease Huanglongbing (HLB), which is vectored by the Asian citrus psyllid. The model is used to evaluate area-wide coordinated spraying when free-riding is possible given individuals’ beliefs in other grower participation in area-wide spraying and in the information provided by extension on the threat as HLB spread.
Consumer diets and values ABM
Natalie Davis Merlin Radbruch Dean Bucciarelli | Published Thursday, December 22, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, March 05, 2025An agent-based model of individual consumers making choices between five possible diets: omnivore, flexitarian, pescatarian, vegetarian, or vegan. Each consumer makes decisions based on personal constraints and values, and their perceptions of how well each diet matches with those values. Consumers can also be influenced by each other’s perceptions via interaction across three social networks: household members, friends, and acquaintances.
ABM Code: Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries
Diego Leal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2025The code and data in this repository are associated with the article titled: “Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries.” The NetLogo code (version 6.4.0) is designed to be a standalone piece of code although it uses the ‘nw’ and ‘matrix’ extensions that come integrated with NetLogo 6.4.0. The code was ran on a Windows 10 x 64 machine.
The NetLogo HIV Spread Model Exploring Impact of PrEP Indication Guidelines
Uri Wilensky Wouter Vermeer Arthur Hjorth | Published Friday, June 05, 2020This agent-based model was built as part of a replication effort of Jeness et al.’s work (linked below). The model simulates an MSM sexual activity network for the purpose of modeling the effects of respectively PrEP and ART on HIV prevention. The purpose of the model is to explore the differences between differerent interpretations of the NIH Indication Guidelines for PrEP.
Zero, Some, or Zero-Sum: Exploring Trade-Offs in Identifying Human Trafficking Among Migration Flows
Kyle Ballard | Published Saturday, September 23, 2017The model attempts to explore the trade-offs between immigration policies and successfully identifying human trafficking victims.
RefugeePathSIM Model
Liliana Perez Saeed Harati Guillaume Arnoux Hébert | Published Thursday, October 11, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, October 16, 2018RefugeePathSIM is an agent-based model to simulate the movement behavior of refugees in order to identify pathways of forced migration under crisis. The model generates migrants and lets them leave conflict areas for a destination that they choose based on their characteristics and desires. RefugeePathSIM has been developed and applied in a study of the Syrian war, using monthly data in years 2011-2015.
The code shared here accompanies the paper at https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208451. It simulates the effects of various economic trade scenarios on the phenomenon of the ‘disappearing middle’ in the Scottish beef and dairy farming industries. The ‘disappearing middle’ is a situation in which there is a simultaneous observed decline in medium-sized enterprises and rise in the number of small and large-scale enterprises.
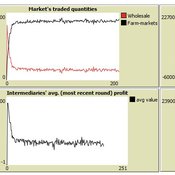
Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia.
César García-Díaz | Published Sunday, April 12, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 12, 2020This a model developed as a part of the paper Mejía, G. & García-Díaz, C. (2018). Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia. Agricultural Systems 160: 132-142.
It simulates the competition dynamics of the potato market in Bogotá, Colombia. The model explores the economic impact of intermediary actors on the potato supply chain.
An agent-based model for assessing strategies of adaptation to climate and tourism demand changes in an alpine destination
Stefano Balbi Marco Alberti | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is then used for assessing three hypothetical and contrasted infrastructure-oriented adaptation strategies for the winter tourism industry, that have been previously discussed with local stakeholders, as possible alternatives to the “business-as-usual” situation.
Peer reviewed ABM Overtourism Santa Marta
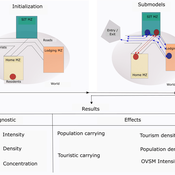
Janwar Moreno | Published Monday, October 23, 2023This model presents the simulation model of a city in the context of overtourism. The study area is the city of Santa Marta in Colombia. The purpose is to illustrate the spatial and temporal distribution of population and tourists in the city. The simulation analyzes emerging patterns that result from the interaction between critical components in the touristic urban system: residents, urban space, touristic sites, and tourists. The model is an Agent-Based Model (ABM) with the GAMA software. Also, it used public input data from statistical centers, geographical information systems, tourist websites, reports, and academic articles. The ABM includes assessing some measures used to address overtourism. This is a field of research with a low level of analysis for destinations with overtourism, but the ABM model allows it. The results indicate that the city has a high risk of overtourism, with spatial and temporal differences in the population distribution, and it illustrates the effects of two management measures of the phenomenon on different scales. Another interesting result is the proposed tourism intensity indicator (OVsm), taking into account that the tourism intensity indicators used by the literature on overtourism have an overestimation of tourism pressures.
Displaying 10 of 810 results for "Jon Solera" clear search