About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 983 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search
Retention in Higher Education: An Agent-Based Model of Social Interactions and Motivated Agent Behavior
Andrew Crooks Amira Al-Khulaidy Stine | Published Wednesday, October 23, 2024Educational attainment and student retention in higher education are two of the main focuses of higher education research. Institutions in the U.S. are constantly looking for ways to identify areas of improvement across different aspects of the student experience on university campuses. This paper combines Department of Education data, U.S. Census data, and higher education theory on student retention, to build an agent-based model of student behavior.
An agent-based model to simulate the impact of developers’ capital possession on urban development
Agung Wahyudi | Published Saturday, June 23, 2018The model combines agent-based modelling and microeconomic approach to simulate the decision behaviour of land developers and how this impacts on the spatio-temporal processes of urban expansion.
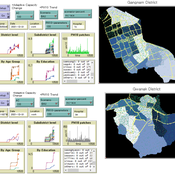
An Agent-based Assessment of Health Vulnerability to Long-term particulate exposure in Seoul Districts
Hyesop Shin Mike Bithell | Published Monday, November 05, 2018 | Last modified Monday, December 03, 2018This model aims to understand the cumulative effects on the population’s vulnerability as represented by exposure to PM10 (particulate matter with diameter less than 10 micrometres) by different age and educational groups in two Seoul districts, Gangnam and Gwanak. Using this model, readers can explore individual’s daily commuting routine, and its health loss when the PM10 concentration of the current patch breaches the national limit of 100µg/m3.
Confirmation Bias improves Performance in a Signal Detection Task and evolves in an Evolutionary Algorithm
Michael Vogrin | Published Monday, May 08, 2023Confirmation Bias is usually seen as a flaw of the human mind. However, in some tasks, it may also increase performance. Here, agents are confronted with a number of binary Signals (A, or B). They have a base detection rate, e.g. 50%, and after they detected one signal, they get biased towards this type of signal. This means, that they observe that kind of signal a bit better, and the other signal a bit worse. This is moderated by a variable called “bias_effect”, e.g. 10%. So an agent who detects A first, gets biased towards A and then improves its chance to detect A-signals by 10%. Thus, this agent detects A-Signals with the probability of 50%+10% = 60% and detects B-Signals with the probability of 50%-10% = 40%.
Given such a framework, agents that have the ability to be biased have better results in most of the scenarios.
DIAL is a model of group dynamics and opinion dynamics. It features dialogues, in which agents put their reputation at stake. Intra-group radicalisation of opinions appears to be an emergent phenomenon.
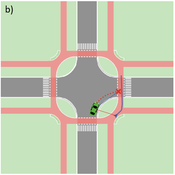
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
Simulating the evolution of the human family
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2017The (cultural) evolution of cooperative breeding in harsh environments.
Social and ecological feedback in greening behavior
Athena Aktipis | Published Thursday, February 19, 2015We construct an agent-based model to investigate and understand the roles of green attachment, engagement in local ecological investment (i.e., greening), and social feedback.
Peer reviewed A model of environmental awareness spread and its effect in resource consumption reduction
Giovanna Sissa | Published Sunday, June 21, 2015 | Last modified Monday, August 17, 2015The model reproduces the spread of environmental awareness among agents and the impact of awareness level of the agents on the consumption of a resource, like energy. An agent is a household with a set of available advanced smart metering functions.
Towards an Agent-Based Model for Civil Revolution: Modeling Emergence of Protesters, Military Decisions, and Resulting State of
Salwa Ismail | Published Friday, August 18, 2017This paper builds on a basic ABM for a revolution and adds a combination of behaviors to its agents such as military benefits, citizen’s grievances, geographic vision, empathy, personality type and media impact.
Displaying 10 of 983 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search