About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search
Simulation model replicating the five different games that were run during a workshop of the TISSS Lab
tissslab | Published Friday, April 30, 2021The three-day participatory workshop organized by the TISSS Lab had 20 participants who were academics in different career stages ranging from university student to professor. For each of the five games, the participants had to move between tables according to some pre-specified rules. After the workshop both the participant’s perception of the games’ complexities and the participants’ satisfaction with the games were recorded.
In order to obtain additional objective measures for the games’ complexities, these games were also simulated using this simulation model here. Therefore, the simulation model is an as-accurate-as-possible reproduction of the workshop games: it has 20 participants moving between 5 different tables. The rules that specify who moves when vary from game to game. Just to get an idea, Game 3 has the rule: “move if you’re sitting next to someone who is waring white or no socks”.
An exact description of the workshop games and the associated simulation models can be found in the paper “The relation between perceived complexity and happiness with decision situations: searching for objective measures in social simulation games”.
Hybrid agent-based methodology for testing response protocols
Fernando Sancho Caparrini | Published Wednesday, February 03, 2021In recent years we have seen multiple incidents with a large number of people injured and killed by one or more armed attackers. Since this type of violence is difficult to predict, detecting threats as early as possible allows to generate early warnings and reduce response time. In this context, any tool to check and compare different action protocols can be a further step in the direction of saving lives. Our proposal combines features from continuous and discrete models to obtain the best of both worlds in order to simulate large and crowded spaces where complex behavior individuals interact. With this proposal we aim to provide a tool for testing different security protocols under several emergency scenarios, where spaces, hazards, and population can be customized. Finally, we use a proof of concept implementation of this model to test specific security protocols under emergency situations for real spaces. Specifically, we test how providing some users of a university college with an app that informs about the type and characteristics of the ongoing hazard, affects in the safety performance.
ACT: Agent-based model of Critical Transitions
Igor Nikolic Oscar Kraan Steven Dalderop Gert Jan Kramer | Published Wednesday, October 18, 2017 | Last modified Monday, August 27, 2018ACT is an ABM based on an existing conceptualisation of the concept of critical transitions applied to the energy transition. With the model we departed from the mean-field approach simulated relevant actor behaviour in the energy transition.
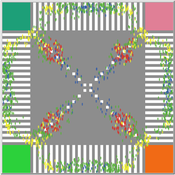
Pedestrian Scramble
Sho Takami Rami Lake Dara Vancea | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025This is a model intended to demonstrate the function of scramble crossings and a more efficient flow of pedestrian traffic with the presence of diagonal crosswalks.
Peer reviewed Horse population dynamics
Nika Galic | Published Tuesday, November 12, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, October 29, 2014This model investigates the link between prescribed growth in body size, population dynamics and density dependence through population feedback on available resources.
02 OamLab V1.10 - Open Atwood Machine Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 13, 2017Using chains of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, this model explores implications of the Maximum Power Principle. It is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, EiLab.
Peer reviewed The Indus Village's Weather model: procedural generation of daily weather
Andreas Angourakis | Published Tuesday, May 13, 2025Overview
The Weather model is a procedural generation model designed to create realistic daily weather data for socioecological simulations. It generates synthetic weather time series for solar radiation, temperature, and precipitation using algorithms based on sinusoidal and double logistic functions. The model incorporates stochastic variation to mimic unpredictable weather patterns and aims to provide realistic yet flexible weather inputs for exploring diverse climate scenarios.
The Weather model can be used independently or integrated into larger models, providing realistic weather patterns without extensive coding or data collection. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, enabling users to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and have greater confidence in their applications.
…
Mast seeding model
Giangiacomo Bravo Lucia Tamburino | Published Saturday, September 08, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Purpose of the model is to perform a “virtual experiment” to test the predator satiation hypothesis, advanced in literature to explain the mast seeding phenomenon.
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
SimPioN - Simulating Path dependence in inter-organisational Networks
Nanda Wijermans Frithjof Stöppler | Published Monday, January 11, 2021The SimPioN model aims to abstractly reproduce and experiment with the conditions under which a path-dependent process may lead to a (structural) network lock-in in interorganisational networks.
Path dependence theory is constructed around a process argumentation regarding three main elements: a situation of (at least) initially non-ergodic (unpredictable with regard to outcome) starting conditions in a social setting; these become reinforced by the workings of (at least) one positive feedback mechanism that increasingly reduces the scope of conceivable alternative choices; and that process finally results in a situation of lock-in, where any alternatives outside the already adopted options become essentially impossible or too costly to pursue despite (ostensibly) better options theoretically being available.
The purpose of SimPioN is to advance our understanding of lock-ins arising in interorganisational networks based on the network dynamics involving the mechanism of social capital. This mechanism and the lock-ins it may drive have been shown above to produce problematic consequences for firms in terms of a loss of organisational autonomy and strategic flexibility, especially in high-tech knowledge-intensive industries that rely heavily on network organising.
…
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search