About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search
Linear Threshold
Kaushik Sarkar | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo implementation of Linear Threshold model of influence propagation.
NetLogo-R-Example for the Inititialisation of Agents with Correlated Random Numbers
Danilo Saft | Published Friday, February 14, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This is a short NetLogo example demonstrating how to initialize 500 agents with 4 correlated parameters each with random values by doing the necessary calculations in the program “R” and retrieving the results.
Schwartz Human Values and the Economic Performance
Marcin Czupryna Bogumił Kamiński | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2023The purpose of the model is to provide an analogy for how the Schwartz values may influence the aggregated economic performance, as measured by: public goods provision, private goods provision and leisure time.
Metaphoria 2019 eternal mutation
Timothy Gooding | Published Sunday, February 24, 2019This model is a modification of Metaphoria 2019, where the monetary system can be run with agents that do not die, but their characteristics are mutated as they are in the mortal population.
Indirect Reciprocity with Contagious Reputation in Large-Scale Small-World Networks
Markus Neumann | Published Sunday, July 26, 2020This repository contains the replication materials for the JASSS submission: ‘Indirect Reciprocity with Contagious Reputation in Large-Scale Small-World Networks’. Further detail on how to run the models is provided in README.txt.
Evaluating Government's Policies on Promoting Smart Metering Diffusion in Retail Electricity Markets
Tao Zhang | Published Monday, December 07, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a market game for evaluating the effectiveness of the UK government’s 2008-2010 policy on promoting smart metering in the UK retail electricity market. We break down the policy into four
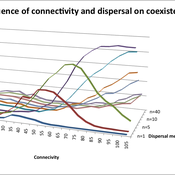
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
Feedback Loop Example: Wildland Fire Spread
James Millington | Published Friday, December 21, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a replication of that described by Peterson (2002) and illustrates the ‘spread’ feedback loop type described in Millington (2013).
The purpose of this model is to enhance a basic ABM through a simple set of rules identified using the activity-driven models in order to produce more realistic patterns of pedestrian movement.
School Enrollment Model
Spiro Maroulis Catalina Canals Enrique Canessa Alejandra Mizala Sergio Chaigneau | Published Monday, July 08, 2024The School Enrollment Model is a spatially-explicit computational model that depicts a city, with schools and students located within the space. The model represents the Chilean school system, a market-based educational system, where people are free to choose among public, private voucher, or private fee-paying schools. In the model, students become aware of some schools, apply to schools, switch schools, pass or fail grade levels, and eventually either graduate or dropout. Schools select students, update their tuition, test scores, and other characteristics.
The purpose of the model is to represent the Chilean school system and analyze the different mechanisms that affected the enrollment distribution between public, private voucher, and private fee-paying school sectors during the period 2004-2016.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search