About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search
Eco-Evolutionary Pathways Toward Industrial Cities
Handi Chandra Putra | Published Thursday, May 21, 2020Industrial location theory has not emphasized environmental concerns, and research on industrial symbiosis has not emphasized workforce housing concerns. This article brings jobs, housing, and environmental considerations together in an agent-based model of industrial
and household location. It shows that four classic outcomes emerge from the interplay of a relatively small number of explanatory factors: the isolated enterprise with commuters; the company town; the economic agglomeration; and the balanced city.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
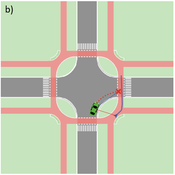
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
CRESY-I stands for CREativity from a SYstems perspetive, Model I. This is the base model in a series designed to describe a systems approach to creativity in terms of variation, selection and retention (VSR) subprocesses.
Influence with over-confident agents
Juliette Rouchier Emily Tanimura | Published Wednesday, October 21, 2015Agents can influence each other if they are close enough in knowledge. The probability to convince with good knowledge and number of agents have an impact on the dissemination of knowledge.
Digital Mobility Model (DMM)
Na (Richard) Jiang Fiammetta Brandajs | Published Thursday, February 01, 2024 | Last modified Friday, February 02, 2024The purpose of the Digital Mobility Model (DMM) is to explore how a society’s adoption of digital technologies can impact people’s mobilities and immobilities within an urban environment. Thus, the model contains dynamic agents with different levels of digital technology skills, which can affect their ability to access urban services using digital systems (e.g., healthcare or municipal public administration with online appointment systems). In addition, the dynamic agents move within the model and interact with static agents (i.e., places) that represent locations with different levels of digitalization, such as restaurants with online reservation systems that can be considered as a place with a high level of digitalization. This indicates that places with a higher level of digitalization are more digitally accessible and easier to reach by individuals with higher levels of digital skills. The model simulates the interaction between dynamic agents and static agents (i.e., places), which captures how the gap between an individual’s digital skills and a place’s digitalization level can lead to the mobility or immobility of people to access different locations and services.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
Peer reviewed Dynamic Value-based Cognitive Architectures
Bart de Bruin | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021The intention of this model is to create an universal basis on how to model change in value prioritizations within social simulation. This model illustrates the designing of heterogeneous populations within agent-based social simulations by equipping agents with Dynamic Value-based Cognitive Architectures (DVCA-model). The DVCA-model uses the psychological theories on values by Schwartz (2012) and character traits by McCrae and Costa (2008) to create an unique trait- and value prioritization system for each individual. Furthermore, the DVCA-model simulates the impact of both social persuasion and life-events (e.g. information, experience) on the value systems of individuals by introducing the innovative concept of perception thermometers. Perception thermometers, controlled by the character traits, operate as buffers between the internal value prioritizations of agents and their external interactions. By introducing the concept of perception thermometers, the DVCA-model allows to study the dynamics of individual value prioritizations under a variety of internal and external perturbations over extensive time periods. Possible applications are the use of the DVCA-model within artificial sociality, opinion dynamics, social learning modelling, behavior selection algorithms and social-economic modelling.
Simulating changing traffic flow caused by new bus route in Augsburg
Eduard | Published Wednesday, August 04, 2021This is a Netlogo model which simulates car and bus/tram traffic in Augsburg, specifically between the districts Stadtbergen, Göggingen and the Königsplatz. People either use their cars or public transport to travel to one of their random destinations (Stadtbergen or Göggingen), performing some activity and then returning to their home. Attributes such as travel and waiting time as well as their happiness upon arriving are stored and have an impact on individuals on whether they would consider changing their mode of transport or not.
A consumer-demand simulation for Smart Metering tariffs (Innovation Diffusion)
Martin Rixin | Published Thursday, August 18, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An Agent-based model simulates consumer demand for Smart Metering tariffs. It utilizes the Bass Diffusion Model and Rogers´s adopter categories. Integration of empirical census microdata enables a validated socio-economic background for each consumer.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search