About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 121 results for "Nathalie Corson" clear search
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
Peer reviewed FishMob: Interactions between fisher mobility and spatial resource heterogeneity
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, October 16, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, June 23, 2020Migration or other long-distance movement into other regions is a common strategy of fishers and fishworkers living and working on the coast to adapt to environmental change. This model attempts to understand the general dynamics of fisher mobility for over larger spatial scales. The model can be used for investigating the complex interplay that exists between mobility and fish stock heterogeneity across regions, and the associated outcomes of mobility at the system level.
The model design informed by the example of small-scale fisheries in the Gulf of California, Mexico but implements theoretical and stylized facts and can as such be used for different archetypical cases. Our methodological approach for designing the model aims to account for the complex causation, emergence and interdependencies in small-scale fisheries to explain the phenomenon of sequential overexploitation, i.e., overexploiting one resource after another. The model is intended to be used as a virtual laboratory to investigate when and how different levels of mobile fishers affect exploitation patterns of fisheries resources.
Peer reviewed COMMONSIM: Simulating the utopia of COMMONISM
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Ernest Aigner Stefan Meretz Jens Schröter Hanno Pahl Annette Schlemm Simon Sutterlütti | Published Sunday, November 05, 2023This research article presents an agent-based simulation hereinafter called COMMONSIM. It builds on COMMONISM, i.e. a large-scale commons-based vision for a utopian society. In this society, production and distribution of means are not coordinated via markets, exchange, and money, or a central polity, but via bottom-up signalling and polycentric networks, i.e. ex-ante coordination via needs. Heterogeneous agents care for each other in life groups and produce in different groups care, environmental as well as intermediate and final means to satisfy sensual-vital needs. Productive needs decide on the magnitude of activity in groups for a common interest, e.g. the production of means in a multi-sectoral artificial economy. Agents share cultural traits identified by different behaviour: a propensity for egoism, leisure, environmentalism, and productivity. The narrative of this utopian society follows principles of critical psychology and sociology, complexity and evolution, the theory of commons, and critical political economy. The article presents the utopia and an agent-based study of it, with emphasis on culture-dependent allocation mechanisms and their social and economic implications for agents and groups.
Peer reviewed MicroAnts 2.5
Diogo Alves | Published Thursday, October 16, 2025MicroAnts 2.5 is a general-purpose agent-based model designed as a flexible workhorse for simulating ecological and evolutionary dynamics in artificial populations, as well as, potentially, the emergence of political institutions and economic regimes. It builds on and extends Stephen Wright’s original MicroAnts 2.0 by introducing configurable predators, inequality tracking, and other options.
Ant agents are of two tyes/casts and controlled by 16-bit chromosomes encoding traits such as vision, movement, mating thresholds, sensing, and combat strength. Predators (anteaters) operate in static, random, or targeted predatory modes. Ants reproduce, mutate, cooperate, fight, and die based on their traits and interactions. Environmental pressures (poison and predators) and social dynamics (sharing, mating, combat) drive emergent behavior across red and black ant populations.
The model supports insertion of custom agents at runtime, configurable mutation/inversion rates, and exports detailed statistics, including inequality metrics (e.g., Gini coefficients), trait frequencies, predator kills, and lineage data. Intended for rapid testing and educational experimentation, MicroAnts 2.5 serves as a modular base for more complex ecological and social simulations.
Adoption of conservation practices
Irem Daloglu | Published Monday, October 21, 2013This model is designed to investigate the impact of alternative policy approaches and changing land tenure dynamics on farmer adoption of conservation practices intended to increase the water quality.
Peer reviewed Torsten Hägerstrand’s Spatial Innovation Diffusion Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a replication of Torsten Hägerstrand’s 1965 model–one of the earliest known calibrated and validated simulations with implicit “agent based” methodology.
A simple emulation-based computational model
Carlos M Fernández-Márquez Francisco J Vázquez | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 05, 2019Emulation is one of the simplest and most common mechanisms of social interaction. In this paper we introduce a descriptive computational model that attempts to capture the underlying dynamics of social processes led by emulation.
An Agent-Based Model of Flood Risk and Insurance
J Dubbelboer I Nikolic K Jenkins J Hall | Published Monday, July 27, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 03, 2016A model to show the effects of flood risk on a housing market; the role of flood protection for risk reduction; the working of the existing public-private flood insurance partnership in the UK, and the proposed scheme ‘Flood Re’.
Heterogeneity of preferences and the dynamics of voluntary contributions to public goods
Engi Amin Amal Soliman Mohamed Abouelela | Published Thursday, August 18, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, January 25, 2018This model simulates the heterogeneity of preferences in a PG game and how the interaction between them affects the dynamics of voluntary contributions. Model is based on the results of a human-based experiment.
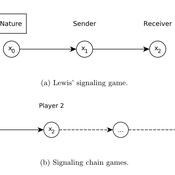
Lewis' Signaling Chains
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
Displaying 10 of 121 results for "Nathalie Corson" clear search