About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Peer reviewed SWIRS Spread of a woody invader in riparian systems
Moira Zellner Beatriz Sosa Carlos Andrés Chiale | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023Riparian forests are one of the most vulnerable ecosystems to the development of biological invasions, therefore limiting their spread is one of the main challenges for conservation. The main factors that explain plant invasions in these ecosystems are the capacity for both short- and long-distance seed dispersion, and the occurrence of suitable habitats that facilitate the establishment of the invasive species. Large floods constitute an abiotic filter for invasion.
This model simulates the spatio-temporal spread of the woody invader Gleditsia. triacanthos in the riparian forest of the National Park Esteros de Farrapos e Islas del Río Uruguay, a riparian system in the coast of the Uruguay river (South America). In this model, we represent different environmental conditions for the development of G. triacanthos, long- and short-distance spread of its fruits, and large floods as the main factor of mortality for fruit and early stages.
Field results show that the distribution pattern of this invasive species is limited by establishment, i.e. it spreads locally through the expansion of small areas, and remotely through new invasion foci. This model recreates this dispersion pattern. We use this model to derive management implications to control the spread of G. triacanthos
Online Protest and Repression in Authoritarian Settings (OPRAS)
Nanda Wijermans Annie Waldherr Aytalina Kulichkina | Published Tuesday, January 27, 2026This agent-based model, developed for the study “Online Protest and Repression in Authoritarian Settings,” examines how online protest and repression evolve in authoritarian contexts and how these dynamics affect ordinary users’ attitudes and behavior on social media. The model integrates key theoretical and empirical insights into social media use and core political factors that shape digital contention in authoritarian settings. The following questions are addressed: (1) how online protest–repression dynamics unfold across different levels of authoritarianism and varying compositions of committed accounts, and (2) how ordinary users’ internal propensity to protest and their perceived probability of successful repression change during online protest-repression contestation. The model is evaluated against two empirically grounded macro patterns observed in the real world. The first is enduring protest: online protest becomes dominant as vocal protesters grow to outnumber vocal repressors, shrinking the pool of silent users and stabilizing a pro-protest majority. The second is suppressed protest: online dissent is contained as vocal repression and silence expand in response to protest, yielding a sustained majority of repressive and silent accounts. Together, these dynamics demonstrate how dissenting voices are empowered and suppressed online in authoritarian settings.
BENCHv.2 model
Leila Niamir | Published Sunday, April 28, 2019The BENCH agent-based model is designed and developed to study shifts in residential energy use and corresponding emissions driven by behavioral changes among heterogeneous individuals.
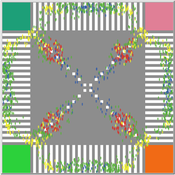
Pedestrian Scramble
Sho Takami Rami Lake Dara Vancea | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025This is a model intended to demonstrate the function of scramble crossings and a more efficient flow of pedestrian traffic with the presence of diagonal crosswalks.
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
Peer reviewed Labor and environment in global value chains: An evolutionary policy study with a three-sector and two-region agent-based macroeconomic model
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Bernhard Rengs | Published Wednesday, December 22, 2021With this model, we investigate resource extraction and labor conditions in the Global South as well as implications for climate change originating from industry emissions in the North. The model serves as a testbed for simulation experiments with evolutionary political economic policies addressing these issues. In the model, heterogeneous agents interact in a self-organizing and endogenously developing economy. The economy contains two distinct regions – an abstract Global South and Global North. There are three interlinked sectors, the consumption good–, capital good–, and resource production sector. Each region contains an independent consumption good sector, with domestic demand for final goods. They produce a fictitious consumption good basket, and sell it to the households in the respective region. The other sectors are only present in one region. The capital good sector is only found in the Global North, meaning capital goods (i.e. machines) are exclusively produced there, but are traded to the foreign as well as the domestic market as an intermediary. For the production of machines, the capital good firms need labor, machines themselves and resources. The resource production sector, on the other hand, is only located in the Global South. Mines extract resources and export them to the capital firms in the North. For the extraction of resources, the mines need labor and machines. In all three sectors, prices, wages, number of workers and physical capital of the firms develop independently throughout the simulation. To test policies, an international institution is introduced sanctioning the polluting extractivist sector in the Global South as well as the emitting industrial capital good producers in the North with the aim of subsidizing innovation reducing environmental and social impacts.
The SAFIRe model : Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food security, and Reforestation
Etienne DELAY Lucas Broutin | Published Thursday, June 12, 2025The SAFIRe model (Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food Security, and Reforestation) is an agent-based model co-developed with rural communities in Senegal’s Groundnut Basin. Its purpose is to explore how local farming and pastoral practices affect the regeneration of Faidherbia albida trees, which are essential for maintaining soil fertility and supporting food security through improved millet production. The model supports collective reflection on how different social and ecological factors interact, particularly around firewood demand, livestock pressure, and agricultural intensification.
The model simulates a 100-hectare agricultural landscape where agents (farmers, shepherds, woodcutters, and supervisors) interact with trees, land parcels, and each other. It incorporates seasonality, crop rotation, tree growth and cutting, livestock feeding behaviors, and farmers’ engagement in sapling protection through Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR). Two types of surveillance strategies are compared: community-led monitoring and delegated surveillance by forestry authorities. Farmer engagement evolves over time based on peer influence, meeting participation, and the success of visible tree regeneration efforts.
SAFIRe integrates participatory modeling (ComMod and ComExp) and a backcasting approach (ACARDI) to co-produce scenarios rooted in local aspirations. It was explored using the OpenMole platform, allowing stakeholders to test a wide range of future trajectories and analyze the sensitivity of key parameters (e.g., discussion frequency, time in fields). The model’s outcomes not only revealed unexpected insights—such as the hidden role of farmers in tree loss—but also led to real-world actions, including community nursery creation and behavioral shifts toward tree care. SAFIRe illustrates how agent-based modeling can become a tool for social learning and collective action in socio-ecological systems.
Netlogo Profiler code example
Colin Wren | Published Wednesday, March 04, 2015This is a very simple foraging model used to illustrate the features of Netlogo’s Profiler extension.
WatASit
Bastien RICHARD Bastien Richard Isabelle Braud Bruno Bonté Olivier Barreteau | Published Friday, December 20, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, October 28, 2020WatASit is an agent-based model implemented in the CORMAS plateform. The model is developped to simulate irrigation situations at the operational level during a collective irrigation campaign.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search