About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results
Simulation model for compliance behaviour
Esther Van Asselt Sjoukje A Osinga | Published Friday, October 03, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, December 08, 2015This model can be used to optimize intervention strategies for inspection services.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
Emerging innovation niches model
Antonio Lopolito Richard Taylor Piergiuseppe Morone | Published Monday, September 22, 2014Objective of our model is to simulate the emergence and operation of a technological niches (TN) in terms of actors’ interaction. A TN can be conceived as protected socio-economic space where radical innovations are developed and tested
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
IDEAL
Arika Ligmann-Zielinska | Published Thursday, August 07, 2014IDEAL: Agent-Based Model of Residential Land Use Change where the choice of new residential development in based on the Ideal-point decision rule.
Informal City version 1.0
Nina Schwarz | Published Friday, July 25, 2014 | Last modified Thursday, July 30, 2015InformalCity, a spatially explicit agent-based model, simulates an artificial city and allows for testing configurations of urban upgrading schemes in informal settlements.
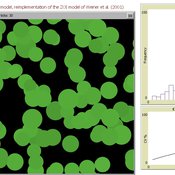
Peer reviewed AZOI: Another Zone Of Influence model
Cyril Piou | Published Wednesday, July 23, 2014 | Last modified Thursday, December 11, 2014This model reimplement Weiner et al. 2001 Zone Of Influence model to simulate plant growth under competition. The reimplementation in Netlogo and the ODD description in the “info” tab try to be as consistent as possible with the original paper.
Modelling Academics as Agents: An Implementation of an Agent-Based Strategic Publication Model
Keith Nesbitt Xin Gu David Cornforth Karen Blackmore | Published Wednesday, July 23, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, July 13, 2022The purpose of this agent-based model is to explore the emergent phenomena associated with scientific publication, including quantity and quality, from different academic types based on their publication strategies.
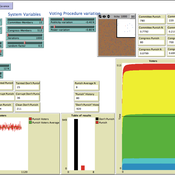
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results